Guides to Blockchain Nodes and Crypto Mining
This is THE Hottest Passive Crypto Mining Right Now. Period.
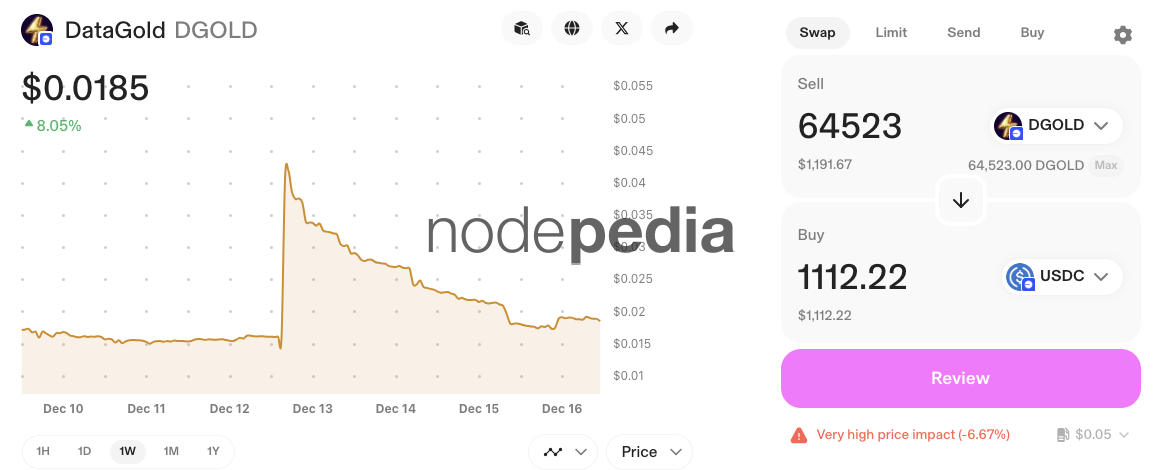
Stake a small amount of 0.005 ETH (which you can withdraw at any time) to start mining $dGOLD tokens. These tokens can be instantly sold on Uniswap, a popular decentralized exchange.
You can’t make this up!
More ETH staked »» more $dGOLD mined without any lock-in period, meaning you can withdraw your ETH anytime if you decide you need it elsewhere.
Here’s a real-life example: With just ~2 ETH, I mined 1,112 $USDC 🚀 worth of $DGOLD in a week. And if I had sold on December 13th, when the value surged, I could have earned even more. That’s the potential of this opportunity. 👉 Continue reading here 👈
Blockchain Nodes Explained: Types, Benefits, and the Latest Trends in AI Mining
Guides: GPU Rental | Nimble Mining | Rivalz Mining
Blockchain technology is at the core of cryptocurrencies and many decentralized applications. A fundamental component of this technology is the blockchain node, which maintains the integrity and functionality of the network.
What Are Blockchain Nodes?
A blockchain node is a device, typically a computer, that participates in a blockchain network. Nodes are responsible for validating transactions, maintaining a copy of the blockchain ledger, and ensuring the network’s security and decentralization. They communicate with each other to form the backbone of a decentralized network, ensuring the blockchain operates smoothly and reliably.
Different Types of Blockchain Nodes
Full Nodes:
- Store the entire history of the blockchain and validate transactions and blocks.
- Examples include Bitcoin Core and Ethereum Geth.
Light Nodes:
- Store only part of the blockchain and rely on full nodes for transaction verification.
- Examples include mobile wallets like Electrum (Bitcoin) and MetaMask (Ethereum).
Masternodes:
- Provide additional services like transaction mixing and instant transactions, typically requiring a significant amount of collateral.
- Examples include Dash Masternodes.
Staking Nodes:
- Used in Proof of Stake (PoS) networks to validate transactions based on the number of coins staked by the node operator.
- Examples include Cardano and Tezos.
AI Nodes:
- Integrate artificial intelligence to enhance functionalities such as predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Examples include projects like SingularityNET.
Why Run a Blockchain Node?
Running a blockchain node offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Operating your own node allows you to verify transactions independently, boosting security.
- Increased Privacy: Direct interaction with the blockchain enhances privacy by reducing reliance on intermediaries.
- Network Support: By running a node, you contribute to the decentralization and robustness of the network.
- Earning Rewards: Some networks offer rewards for running nodes, such as transaction fees or newly minted coins.
Running Nodes: Hardware vs. Cloud-Based Services
Own Hardware:
- Pros: Full control over the node, enhanced privacy, potentially lower long-term costs.
- Cons: Requires significant initial investment, ongoing maintenance, and technical expertise.
Cloud-Based Services:
- Pros: Easy setup, scalable, managed services reduce the need for technical expertise.
- Cons: Higher ongoing costs, less control.
What Are Node Sales?
Node sales refer to the process of selling access or ownership of blockchain nodes. This can include physical nodes, virtual nodes, or staking nodes. Node sales provide an accessible entry point for individuals and organizations to participate in blockchain networks without needing to set up and maintain the hardware themselves.
Crypto Mining Nodes
Crypto mining nodes are specialized nodes used in Proof of Work (PoW) blockchain networks. These nodes perform complex calculations to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain, a process known as mining. Successful miners are rewarded with cryptocurrency. Popular examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum (prior to its transition to PoS).
- ASIC Miners: Application-Specific Integrated Circuits designed for mining specific cryptocurrencies.
- GPU Miners: Graphics Processing Units used for mining various cryptocurrencies.
AI Mining Nodes: The New Trend
AI mining nodes represent an innovative trend where blockchain nodes are utilized for AI training tasks. Node operators contribute their computational resources to train large language models (LLMs) and other AI algorithms, often requiring powerful GPUs like those from Nvidia. In return for their computational contributions, operators are rewarded in cryptocurrency.
One prominent example of this emerging trend is the Nimble Network. Nimble leverages decentralized GPU resources to perform AI training tasks, rewarding participants with NIM tokens for their contributions. This model democratizes access to AI training resources and incentivizes broader participation in the AI development ecosystem.
Conclusion
Blockchain nodes are essential for the functioning and security of decentralized networks. Understanding the different types of nodes, the benefits of running a node, and the emerging trends like AI mining nodes can help you make informed decisions about participating in the blockchain ecosystem. Whether you’re considering setting up a node on your hardware, using cloud-based services like Runpod, Vast, and Clore, or exploring the latest trends in AI and crypto mining, being a node operator is a significant step towards embracing the future of decentralized technology.